Electro-less Plating
Electro-less Plating
 |
| https://www.sharrettsplating.com/coatings/electroless-nickel |
In this blog, we will take a look to the
Questions:
●
What is Electroless Plating?
●
What makes it different from
Electro-Plating?
●
What factors affect
the Plating Quality?
●
What are its Advantages and
Disadvantages?
● What are the Applications
Electro-less
Plating:
Electro-less Plating is a class of industrial
chemical processes that create metal coating on various materials by
autocatalytic chemical reduction of metal cations in liquid bath. It is also
known as Chemical Plating or Autocatalytic Plating
The story of Electro-less plating begins in 1946
at the 34th Annual AES Meeting, when Abner Brenner and Grace Riddell of the
National Bureau of Standards disclose results of their studies on experimental Nickel electroplating baths. They had
attempted to prevent undesirable oxidation of bath constituents at the inert
anode by making additions of reducing agents to the bath. As luck would have
it, one of the reducing agents explored was sodium hypophosphite. Surprisingly, the amount of nickel deposited exceeded
the amount theoretically limited by Faraday's law.
They soon found out that nickel deposition
occurred even when no external current
was applied. It was clearly seen that metal deposition was achieved by chemical
reduction but, uniquely, the nickel deposit was itself catalytic for continued reduction. The process was thus
described as autocatalytic chemical reduction of metal ions to form a metal deposit.
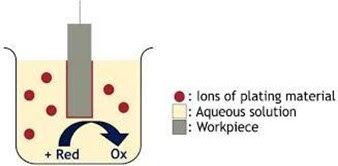
What makes
it different from Electro-Plating?
●
Electro-Plating involves passing of
electric current from the bath and the substrate for reduction of Metal cations
(in the solution) to occur. i.e. transfer of electrons occur due to potential
difference applied.
●
While, in Electro-less Plating, the
Reduction of Metal cations (from the solution) occur purely by means of
Chemical Reduction. i.e. electrons are provided by the oxidation of a Reducing
Agent.
The general reaction of Electro-less Plating
is
Mz+(aq) + Xz-(aq)
where M represents the metal, Xz- the reducing agent, and Z its
oxidized byproducts
 |
| https://interplex.com/wp-content/uploads/Technical-Bulletin-Electroplating-Electroless-Plating-Differences-Benefits.pdf |
In order for the metal to be deposited as
a uniform solid coating on the intended surface, rather than a precipitate
through the solution, the reaction must require a catalyst that is either the
substrate itself or is applied to it beforehand. In fact, the reaction must be
autocatalytic, so that it can continue after the substrate has been coated by
the metal.
Other
Materials which can be used for Electro-less Plating:
●
Nickel-Phosphorous as alloy
●
Nickel-Gold as alloy
●
Nickel-Boron as alloy
● Palladium as alloy
● Copper
Electro-less nickel plating uses nickel salts as the metal cation source and either hypophosphite (or a borohydride-like compound) as the Reducer. A byproduct of the reaction is elemental phosphorus (or boron) which is incorporated in the coating. Tollens' reagent is a classical example of electro-less silver plating. For other metals like gold and copper, the reducing agent is typically a low-molecular-weight aldehyde.
What factors affect plating quality?
Plating
Quality is affected by several factors out of which majority should be taken
care of during Surface Finishing.
Surface preparation:
Rough, badly machined surfaces with uneven metal surfaces, burrs or cold shuts
cannot be effectively plated.
Cleaning: The surface should free form oils,
dirt and soaps formed by saponification of oils by alkaline cleaners.
Control of the plating baths: Temperature, pH, nickel ion concentration and hypophosphite concentration all need to be effectively managed to ensure high quality, consistent plating finish.
Advantages of Electroless Plating:
Electro-less plating has an upper hand over electrolytic plating.
They are
1. Uniformity
With Electro-less plating, the coating deposits on the surface more
evenly, but the thickness of the coating is quite thin as compared to Electrolytic
plating. This even coating can be justified by the fact that deciding factor in
how thick the coating applies to the surface depends on the base’s contact with
the solution, every surface has the same amount of metal coated to it.
 |
| https://maf.com/2016/11/22/electroless-nickel-plating-explained/ |
2. Durability
A layer of nickel-phosphorous plated onto an object with electroless plating provides superior strength for the item it covers. .
3. No Conductivity Required
Electro-less plating can be done on Non-Conducting Surfaces. Thus, Plastics can be uniformly coated.
Disadvantages of Electro-less Plating:
Even though Electro-less plating has many benefits, this method will not be suitable for all uses. Only your project parameters will help you determine the answer.
Limited Bath Life
In Electro-less plating, metals ions are supplied by the bath instead of a metal piece, eventually the bath will run out of metal ions and so needs to be changed.
This will require Regularly Monitoring the liquid and adding solution as required which will in turn increases the cost and complexity of autocatalytic plating.
Applications:
Electro-less Plating find its application in many industrial
sectors to achieve durable, corrosion resistant nickel coating on their
products.
Few of them are mentioned below:
● Automotive Industry:
Engine components that are exposed to elevated temperatures and
regular use require a durable exterior which can be achieved from electro-less
nickel plating.
● Manufacturing:
Molds,
machine parts, dies and more are protected from corrosion and wear by the
application of Electro-less nickel coating in any manufacturing setting.
●
Aerospace Industry:
Same as the automotive industry, the aerospace sector requires
heat- and rust-resistant parts in the engine and throughout the aircraft.
Nickel plating is one of the way to attain the durability needed for these
components.
● Petrochemical Industry:
Petrochemical plants regularly need replacement valves, pipes, plugs and more. A long-lasting nickel coating withstands the heavy friction these parts may experience while protecting the components against corrosion. Thus, increases their life-span.
Blog Credit:
Praful Sunil Kadam (TY Metallurgy and Material Science, 111911029)
(Team Meta Monday)
References:
https://monroeengineering.com/blog/electroplating-vs-electroless-plating-whats-the-difference/
https://www.sharrettsplating.com/blog/electroless-autocatalytic-vs-electrolytic-plating/
https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fmaf.com%2F2016%2F11%2F22%2Felectroless-nickel-plating-explained%2F&psig=AOvVaw1dJOAaenck98XCYG6tUwaT&ust=1641212590610000&source=images&cd=vfe&ved=0CAsQjRxqFwoTCNjwxMWHk_UCFQAAAAAdAAAAABAD
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electroless_plating
https://encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcSpPEtI9I02H7XQv7B2-k-fhXq9UUVtcEcIlw&usqp=CAU
NASF SURFACE TECHNOLOGY WHITE PAPERS
(Historical Highlights of Electroless Plating by
Charles R. Shipley, Jr.)


Comments
Post a Comment